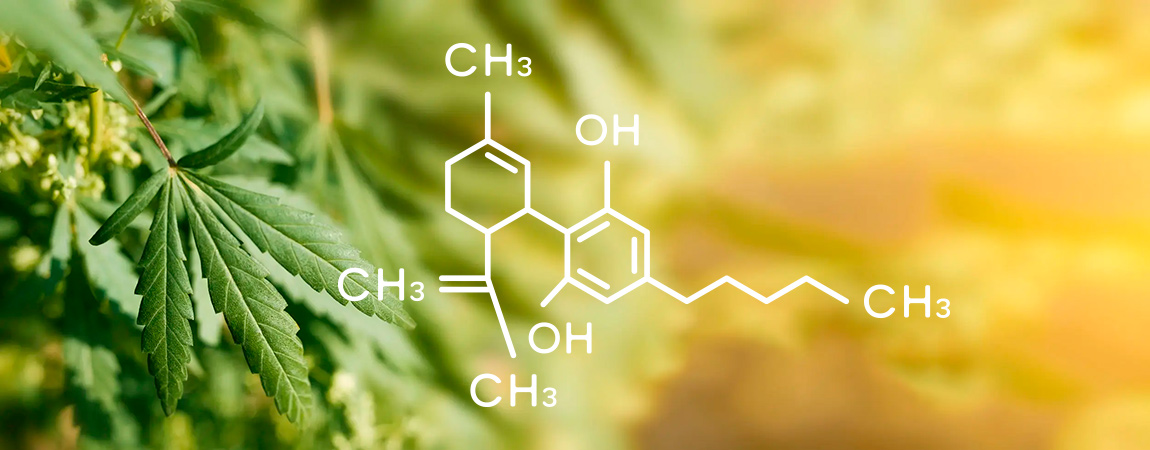
CBD and the endocannabinoid system
Discovered in 1992, the endocannabinoid system is common to all mammals, including us. This system is composed of neurotransmitters (such as serotonin and anandamide) and their corresponding cellular receptors (the best known are called CB1 and CB2).
Phytocannabinoids – or cannabinoids – are compounds present exclusively in the Cannabis sativa species, which help modulate the endocannabinoid system by binding to the CB1 and CB2 receptors, and their consequent activation. These molecules, together with the endocannabinoids that our organism produces naturally, are responsible for the regulation and proper functioning of the endocannabinoid system (hence the name of such system).
The endocannabinoid system plays a significant role in our body, regulating pain sensation, stress, memory, emotions, mood, motor function, nausea, appetite, blood pressure, glucose metabolism, bone density, intestine, immune system and peripheral nervous system. Consequently, a malfunction of the endocannabinoid system can lead to multiple problems such as chronic insomnia and stress, anxiety, depression, autoimmune diseases, epilepsy, cardiovascular diseases, PTSD, chronic diseases… among others.
As scientists Pal Pacher and George Kunos affirm in their study published in May 2013: “modulating the activity of the endocannabinoid system may have therapeutic potential in almost all diseases that affect human
Properties and uses of CBD
The properties of CBD are supported by numerous clinical studies, most of them carried out in the last decade. Scientific articles dealing with the subject explain that CBD could act as:
- Anticonvulsant: reduces the intensity and frequency of seizures
- Antiemetic: reduces nausea and vomiting.
- Appetite stimulant – very effective for chemotherapy patients
- Reduces blood pressure : the combination of its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and relaxing properties is an ideal protection for the heart.
- Immuno-modulator: helps regulate the functioning of the immune system.
- Antioxidant: counteracts cellular aging, preventing the development of diseases such as cancer, myocardial infarction, stroke and neurodegenerative processes.
- Neuroprotective: prevents and delays the degeneration of the nervous system. Protects neurons from degeneration and death.
- Antidepressant and anxiolytic: to treat the symptoms of anxiety, depression, as well as the symptoms of PTSD.
- Antipsychotic: for the treatment of psychosis, especially in cases of schizophrenia, it helps to control hallucinations; it also has the potential to treat manic episodes in bipolar disorders.
- Helps control compulsive thoughts and attitudes: so it can be used to help with addiction problems to other substances or other dependencies such as gambling or technology.
- Anti-inflammatory: reduces inflammation
- Analgesic: relieves pain
- Muscle relaxant: helps combat stiffness in muscles and tendons.
- It stimulates the growth of bones, also strengthens the skeleton of people affected by osteoporosis.
- It is useful to combat insomnia: thanks to its intense calming effect.
CBD could also serve as a palliative for the discomfort that may be caused by certain medical conditions, or their respective treatments (such as chemotherapy, for example). Recent research has shown that this phytocannabinoid possesses qualities that could help alleviate the symptoms of the following disorders:
- Autoimmune disorders:inflammation, rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis
- Neurological disorders:Alzheimer’s, dementia, Parkinson’s, multiple sclerosis, neuralgia, epilepsy, Huntington’s chorea, traumatic brain injuries
- Metabolic syndromes: diabetes, obesity
- Neuropsychiatric disorders:autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, alcoholism
- Intestinal disorders:colitis, Crohn’s disease
- Cardiovascular disorders:atherosclerosis, arrhythmia. Helps prevent heart and brain attacks
- Skin conditions:acne, dermatitis, psoriasis. Helps reduce the production of sebum, inflammatory cytokines, and bacteria
With regard to possible unwanted side effects, it has been shown that CBD can cause sedation and, in large doses, some people may experience diarrhea and/or dizziness. On the other hand, it is possible that it may interact with some medications reinforcing or inhibiting their action; therefore, it is always necessary to consult a doctor if it is combined with pharmacological treatments.
Sources:
SEIC: Spanish Society for Cannabinoid Research
IACM: International Association for Cannabis as Medicine
Project CBD: California-based non-profit organization dedicated to promoting and disseminating the medicinal uses of CBD
WHO Cannabidiol Report, published in November 2017: https://www.who.int/medicines/access/controlled-substances/5.2_CBD.pdf
“6 proven indications for your health of hemp oil”, article published in January 2020; informative portal Cuerpomente. https://www.cuerpomente.com/salud-natural/terapias-naturales/aceite-cbd-marihuana-indicaciones-beneficios-efectos-secundarios_2221
“Modulating the endocannabinoid system in human health and disease: successes and failures”. Pál Pacher and George Kunos, essay published in May 2013; US National Library of the National Institutes of Health: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3684164/